libreboot website (markdown files). https://libreboot.org/
List of commits:
| Subject | Hash | Author | Date (UTC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| re-organise the pico flashing instructions | 5443cd0d05bcd79a24579780baafd8f13ef654d9 | Leah Rowe | 2025-01-08 17:22:26 |
| t480 page: mention the newer patchset used | e10c9b80f016ffccd4a6aa687e5d92aee2562f5b | Leah Rowe | 2025-01-08 03:40:12 |
| mention dependencies on nvmutil.md | 315f4cd6b26640d2306cf3af51f5f77094e07d48 | Leah Rowe | 2025-01-07 15:17:31 |
| document ./mk inject setmac on the nvmutil page | d120ebf8f2dd87a3db0768eb45dc773228ddcefb | Leah Rowe | 2025-01-07 08:33:39 |
| nvmutil: Remove redundant information | a6478d6797236e86a765efb24c92d3ae3b711434 | Leah Rowe | 2025-01-07 04:42:16 |
| formatting | 090e58d4f84125bdcf035efcadd1cd5c13a03c77 | Leah Rowe | 2025-01-06 21:42:50 |
| Libreboot 20241206, 8th revision (announcement) | 1b4326dd620f7b770e3d68c34c96623e86d84e5b | Leah Rowe | 2025-01-06 21:30:57 |
| Add missing release year to ASUS KFSN4-DRE | 7421e9a8c7a7b6aa5a6e70294973ea4fd4bedb77 | libreandre | 2025-01-06 16:18:26 |
| docs/build: Remove the python instructions | c1daf0fc5ec42fac72c3d608a4c112770edbf97a | Leah Rowe | 2025-01-05 22:21:49 |
| list angel pons on contrib.md (haswell nri) | 6a8e230d7a2543282c1f9a50b86259a98decf11a | Leah Rowe | 2025-01-05 20:13:51 |
| clean up references to who.md | fcb63c3c3b5673aa2afafbe9fe7702eaa4f10d55 | Leah Rowe | 2025-01-05 18:16:16 |
| Vastly expanded the contrib page | fd1a0ae3a2b3915abfafbf31baa233e2d4e034c2 | Leah Rowe | 2025-01-05 18:09:14 |
| rename contact-fr.md to contact.fr.md | 7fddfaca820d075bf31dc60548b8b62825bacabd | Leah Rowe | 2025-01-05 12:19:42 |
| further clarification of intent | 90804582a8df8824f82fd1757dd40487ddac34a1 | Leah Rowe | 2025-01-05 12:05:44 |
| docs/maintain: Clearer introduction to PSDG policy | a3158f3f97f949513916b8345a58c7645415cb01 | Leah Rowe | 2025-01-05 12:04:14 |
| ivy_has_common: document setmac restore | 990f55056394103be65119b38f0e37def16fdcef | Leah Rowe | 2025-01-05 11:24:54 |
| ivy_has_common: document setmac keep | a6026556c97d229fb7f43cad10a3d0eee51efbac | Leah Rowe | 2025-01-05 07:58:32 |
| further expand the system requirement info | 43e7f2eff0f5f28103e87037dc28158a9e0e2a8c | Leah Rowe | 2025-01-04 17:31:40 |
| remove duplication | 00dacd33ef28baf4bceb5aa17f823f0bd8100818 | Leah Rowe | 2025-01-04 17:25:11 |
| move system requirements to docs/maintain/ | 9011218a8eeb7f2f3ea89e605f5331c959267f9c | Leah Rowe | 2025-01-04 17:23:02 |
Commit 5443cd0d05bcd79a24579780baafd8f13ef654d9
- re-organise the pico flashing instructions
Author date (UTC): 2025-01-08 17:22
Committer name: Leah Rowe
Committer date (UTC): 2025-01-08 17:22
Parent(s): e10c9b80f016ffccd4a6aa687e5d92aee2562f5b
Signer:
Signing key:
Signing status: N
Tree: 456b554fc8156ead9896b5d0b9928ed14535b644
the instructions were a bit crap, for example it wasn't
clear that you can get the firmawre pre-compiled in libreboot
releases. adapt it accordingly.
Signed-off-by: Leah Rowe <leah@libreboot.org>
Author: Leah Roweclear that you can get the firmawre pre-compiled in libreboot
releases. adapt it accordingly.
Signed-off-by: Leah Rowe <leah@libreboot.org>
Author date (UTC): 2025-01-08 17:22
Committer name: Leah Rowe
Committer date (UTC): 2025-01-08 17:22
Parent(s): e10c9b80f016ffccd4a6aa687e5d92aee2562f5b
Signer:
Signing key:
Signing status: N
Tree: 456b554fc8156ead9896b5d0b9928ed14535b644
| File | Lines added | Lines deleted |
|---|---|---|
| site/docs/install/spi.md | 50 | 21 |
| site/docs/install/spi.zh-cn.md | 62 | 14 |
| File site/docs/install/spi.md changed (mode: 100644) (index 21c6546..90f5f9e) | |||
| ... | ... | is called *external* because it's not the *internal* one on your mainboard. | |
| 67 | 67 | Raspberry Pi Pico | Raspberry Pi Pico |
| 68 | 68 | ================= | ================= |
| 69 | 69 | ||
| 70 | RP2040/RP2530 both supported | ||
| 71 | ---------------------------- | ||
| 72 | |||
| 70 | 73 | **Pico 2 and other RP2530 dongles also supported, on Libreboot 20241206 rev8 | **Pico 2 and other RP2530 dongles also supported, on Libreboot 20241206 rev8 |
| 71 | 74 | or higher. Releases before this only supported the original Pico, and other | or higher. Releases before this only supported the original Pico, and other |
| 72 | 75 | RP2040 dongles; newer Libreboot releases now support both RP2040 and RP2530.** | RP2040 dongles; newer Libreboot releases now support both RP2040 and RP2530.** |
| ... | ... | Additionally, all the software running on it is free, down to the full | |
| 83 | 86 | versions (Pico W & Pico WH) need vendor firmware to use the Wi-Fi chip, | versions (Pico W & Pico WH) need vendor firmware to use the Wi-Fi chip, |
| 84 | 87 | but that is not needed for following this guide. | but that is not needed for following this guide. |
| 85 | 88 | ||
| 86 | A Pico has proper 3.3V logic levels, unlike a ch341a. Which means it won't | ||
| 87 | destroy your board by sending 5V to it. If you have a 1.8V flash chip, | ||
| 88 | you need to add a logic level converter. | ||
| 89 | Download serprog firmware pre-compiled | ||
| 90 | ------------------------- | ||
| 89 | 91 | ||
| 90 | First, connect just the Pico to your computer with a micro-USB cable. | ||
| 91 | Mount it like any other USB flash drive. If it isn't detected, you might need | ||
| 92 | to press the BOOTSEL button while you plug it in (this forces it into the | ||
| 93 | bootloader mode). | ||
| 92 | Download the pico serprog tarball from Libreboot releases. For example, the | ||
| 93 | Libreboot 20241206rev8 one would be | ||
| 94 | named: `libreboot-20241206rev8_pico_serprog.tar.xz` - it's available under | ||
| 95 | the `roms/` directory in each release. With these binaries, you can easily | ||
| 96 | get started. | ||
| 94 | 97 | ||
| 95 | You can download the serprog firmware here:\ | ||
| 98 | Build serprog firmware from source | ||
| 99 | ---------------------------------- | ||
| 100 | |||
| 101 | You can alternatively download the serprog firmware here:\ | ||
| 96 | 102 | <https://codeberg.org/libreboot/pico-serprog>\ | <https://codeberg.org/libreboot/pico-serprog>\ |
| 97 | 103 | or here:\ | or here:\ |
| 98 | 104 | <https://notabug.org/libreboot/pico-serprog> | <https://notabug.org/libreboot/pico-serprog> |
| ... | ... | You can also find the source code for these, under `src/` in Libreboot release | |
| 101 | 107 | archives (source code tarball), and/or under `src/` in `lbmk.git` if downloading | archives (source code tarball), and/or under `src/` in `lbmk.git` if downloading |
| 102 | 108 | using the build instructions below. | using the build instructions below. |
| 103 | 109 | ||
| 104 | Copy the file `rpi-pico-serprog.uf2` into your Pico. To build this firmware, you | ||
| 110 | Alternatively to the binaries, you | ||
| 105 | 111 | could build it yourself or you could also clone `lbmk.git` and [install build | could build it yourself or you could also clone `lbmk.git` and [install build |
| 106 | 112 | dependencies](../build/#first-install-build-dependencies), then inside lbmk, | dependencies](../build/#first-install-build-dependencies), then inside lbmk, |
| 107 | 113 | do: | do: |
| ... | ... | do: | |
| 109 | 115 | ./mk -b pico-serprog | ./mk -b pico-serprog |
| 110 | 116 | ||
| 111 | 117 | This will automatically build the rpi-pico firmware, and the file will be | This will automatically build the rpi-pico firmware, and the file will be |
| 112 | at `bin/serprog_rp2040/serprog_pico.uf2` | ||
| 113 | and `bin/serprog_rp2040/serprog_pico_w.uf2` - images with `pico2` in the | ||
| 118 | at `bin/serprog_pico/serprog_pico.uf2` | ||
| 119 | and `bin/serprog_pico/serprog_pico_w.uf2` - images with `pico2` in the | ||
| 114 | 120 | file name are for the Pico 2, and they can also be used. | file name are for the Pico 2, and they can also be used. |
| 115 | 121 | ||
| 122 | Install the serprog firmware | ||
| 123 | ---------------------------- | ||
| 124 | |||
| 125 | First, connect just the Pico to your computer with a micro-USB cable. | ||
| 126 | Mount it like any other USB flash drive. If it isn't detected, you might need | ||
| 127 | to press the BOOTSEL button while you plug it in (this forces it into the | ||
| 128 | bootloader mode). | ||
| 129 | |||
| 130 | When you have the build, or if you're using a release build, copy the | ||
| 131 | file `.uf2` file into your Pico. You must make sure to build the correct | ||
| 132 | target, or otherwise copy the correct file, because many RP2040 and RP2530 | ||
| 133 | devices exist and Libreboot provides images for **all of them** in the same | ||
| 134 | release tarball. | ||
| 135 | |||
| 136 | **NOTE: Other RP2040/2530 devices will also work. You just have to match | ||
| 137 | the right pins and use the correct firmware file!** | ||
| 138 | |||
| 139 | Logic levels | ||
| 140 | ------------ | ||
| 141 | |||
| 142 | A Pico has proper 3.3V logic levels, unlike a ch341a. Which means it won't | ||
| 143 | destroy your board by sending 5V to it. If you have a 1.8V flash chip, | ||
| 144 | you need to add a logic level converter. **Please ensure that you have matched | ||
| 145 | the voltage of your programmer to the voltage of your chip; both the data lines | ||
| 146 | and power lines to the chip must match.** | ||
| 147 | |||
| 148 | Wiring | ||
| 149 | ------ | ||
| 150 | |||
| 116 | 151 | Disconnect the Pico and proceed to wire it to your | Disconnect the Pico and proceed to wire it to your |
| 117 | 152 | [flash chip](/docs/install/spi.html#identify-which-flash-type-you-have). | [flash chip](/docs/install/spi.html#identify-which-flash-type-you-have). |
| 118 | 153 | ||
| ... | ... | above](https://av.libreboot.org/rpi_pico/pinout_serprog.png) | |
| 125 | 160 |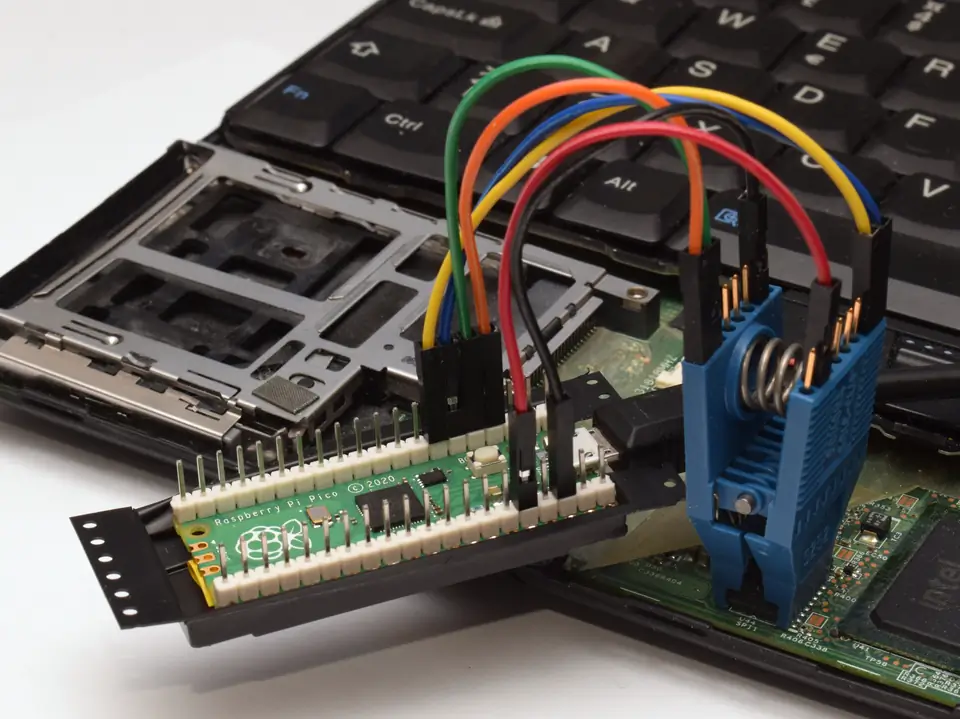  | chip](https://av.libreboot.org/rpi_pico/soic16_x200.webp) |
| 127 | 162 | ||
| 163 | 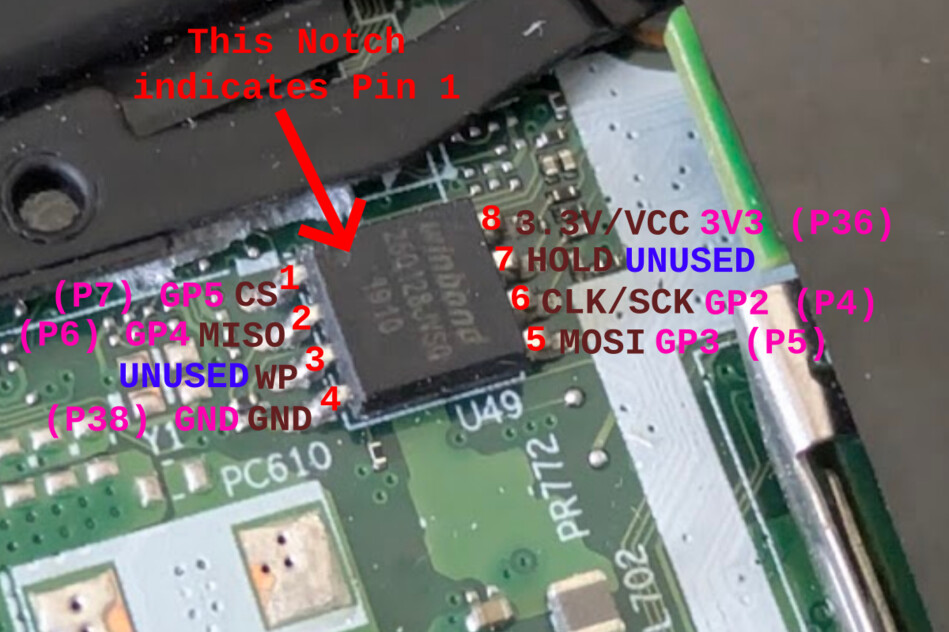 | ||
| 164 | |||
| 128 | 165 | Headers were manually soldered on the top side, and the plastic packaging | Headers were manually soldered on the top side, and the plastic packaging |
| 129 | 166 | was repurposed as an insulating base. These might be nice to have, but by no | was repurposed as an insulating base. These might be nice to have, but by no |
| 130 | 167 | means necessary. If your headers are on the other side, just keep in mind | means necessary. If your headers are on the other side, just keep in mind |
| ... | ... | will appear: | |
| 135 | 172 | ||
| 136 | 173 | [453876.669019] cdc_acm 2-1.2:1.0: ttyACMx: USB ACM device | [453876.669019] cdc_acm 2-1.2:1.0: ttyACMx: USB ACM device |
| 137 | 174 | ||
| 138 | Take note of the ttyACMx. Flashrom is now usable | ||
| 175 | Take note of the ttyACMx. Flashprog is now usable | ||
| 139 | 176 | (substitute ttyACMx with what you observed earlier). | (substitute ttyACMx with what you observed earlier). |
| 140 | 177 | ||
| 141 | 178 | flashprog -p serprog:dev=/dev/ttyACMx,spispeed=16M | flashprog -p serprog:dev=/dev/ttyACMx,spispeed=16M |
| ... | ... | Take note of the ttyACMx. Flashrom is now usable | |
| 143 | 180 | spispeed=32M usually works, but since it's not much faster it's probably | spispeed=32M usually works, but since it's not much faster it's probably |
| 144 | 181 | not worth it. The 12Mbps USB port is limiting the actual speed here. | not worth it. The 12Mbps USB port is limiting the actual speed here. |
| 145 | 182 | ||
| 146 | Raspberry Pi Pico SOIC-8 wiring | ||
| 147 | ------------------------------- | ||
| 148 | |||
| 149 | When using a Raspberry Pi Pico to program a SOIC-8 flash chip with | ||
| 150 | `pico-serprog`, you may use the following diagram, which contains the | ||
| 151 | Raspberry Pi Pins and the pinouts of the typical SOIC-8 chip to wire up | ||
| 152 | your programmer: | ||
| 153 | |||
| 154 |  | ||
| 183 | Higher speeds might work nicely, on Pico 2. | ||
| 155 | 184 | ||
| 156 | 185 | Do not use CH341A! | Do not use CH341A! |
| 157 | 186 | ================== | ================== |
| File site/docs/install/spi.zh-cn.md changed (mode: 100644) (index 46b9abb..bb9b705) | |||
| ... | ... | libreboot 目前记录了这些 SPI 编程器的使用方法: | |
| 43 | 43 | Raspberry Pi Pico | Raspberry Pi Pico |
| 44 | 44 | ================= | ================= |
| 45 | 45 | ||
| 46 | RP2040/RP2530 both supported | ||
| 47 | ---------------------------- | ||
| 48 | |||
| 46 | 49 | **Pico 2 and other RP2530 dongles also supported, on Libreboot 20241206 rev8 | **Pico 2 and other RP2530 dongles also supported, on Libreboot 20241206 rev8 |
| 47 | 50 | or higher. Releases before this only supported the original Pico, and other | or higher. Releases before this only supported the original Pico, and other |
| 48 | 51 | RP2040 dongles; newer Libreboot releases now support both RP2040 and RP2530.** | RP2040 dongles; newer Libreboot releases now support both RP2040 and RP2530.** |
| ... | ... | Additionally, all the software running on it is free, down to the full | |
| 59 | 62 | versions (Pico W & Pico WH) need vendor firmware to use the Wi-Fi chip, | versions (Pico W & Pico WH) need vendor firmware to use the Wi-Fi chip, |
| 60 | 63 | but that is not needed for following this guide. | but that is not needed for following this guide. |
| 61 | 64 | ||
| 62 | A Pico has proper 3.3V logic levels, unlike a ch341a. Which means it won't | ||
| 63 | destroy your board by sending 5V to it. If you have a 1.8V flash chip, | ||
| 64 | you need to add a logic level converter. | ||
| 65 | Download serprog firmware pre-compiled | ||
| 66 | ------------------------- | ||
| 65 | 67 | ||
| 66 | First, connect just the Pico to your computer with a micro-USB cable. | ||
| 67 | Mount it like any other USB flash drive. If it isn't detected, you might need | ||
| 68 | to press the BOOTSEL button while you plug it in (this forces it into the | ||
| 69 | bootloader mode). | ||
| 68 | Download the pico serprog tarball from Libreboot releases. For example, the | ||
| 69 | Libreboot 20241206rev8 one would be | ||
| 70 | named: `libreboot-20241206rev8_pico_serprog.tar.xz` - it's available under | ||
| 71 | the `roms/` directory in each release. With these binaries, you can easily | ||
| 72 | get started. | ||
| 70 | 73 | ||
| 71 | You can download the serprog firmware here:\ | ||
| 74 | Build serprog firmware from source | ||
| 75 | ---------------------------------- | ||
| 76 | |||
| 77 | You can alternatively download the serprog firmware here:\ | ||
| 72 | 78 | <https://codeberg.org/libreboot/pico-serprog>\ | <https://codeberg.org/libreboot/pico-serprog>\ |
| 73 | 79 | or here:\ | or here:\ |
| 74 | 80 | <https://notabug.org/libreboot/pico-serprog> | <https://notabug.org/libreboot/pico-serprog> |
| 75 | 81 | ||
| 76 | Copy the file `rpi-pico-serprog.uf2` into your Pico. To build this firmware, you | ||
| 82 | You can also find the source code for these, under `src/` in Libreboot release | ||
| 83 | archives (source code tarball), and/or under `src/` in `lbmk.git` if downloading | ||
| 84 | using the build instructions below. | ||
| 85 | |||
| 86 | Alternatively to the binaries, you | ||
| 77 | 87 | could build it yourself or you could also clone `lbmk.git` and [install build | could build it yourself or you could also clone `lbmk.git` and [install build |
| 78 | 88 | dependencies](../build/#first-install-build-dependencies), then inside lbmk, | dependencies](../build/#first-install-build-dependencies), then inside lbmk, |
| 79 | 89 | do: | do: |
| ... | ... | do: | |
| 81 | 91 | ./mk -b pico-serprog | ./mk -b pico-serprog |
| 82 | 92 | ||
| 83 | 93 | This will automatically build the rpi-pico firmware, and the file will be | This will automatically build the rpi-pico firmware, and the file will be |
| 84 | at `bin/serprog_rp2040/serprog_pico.uf2` | ||
| 85 | and `bin/serprog_rp2040/serprog_pico_w.uf2` - images with `pico2` in the | ||
| 94 | at `bin/serprog_pico/serprog_pico.uf2` | ||
| 95 | and `bin/serprog_pico/serprog_pico_w.uf2` - images with `pico2` in the | ||
| 86 | 96 | file name are for the Pico 2, and they can also be used. | file name are for the Pico 2, and they can also be used. |
| 87 | 97 | ||
| 98 | Install the serprog firmware | ||
| 99 | ---------------------------- | ||
| 100 | |||
| 101 | First, connect just the Pico to your computer with a micro-USB cable. | ||
| 102 | Mount it like any other USB flash drive. If it isn't detected, you might need | ||
| 103 | to press the BOOTSEL button while you plug it in (this forces it into the | ||
| 104 | bootloader mode). | ||
| 105 | |||
| 106 | When you have the build, or if you're using a release build, copy the | ||
| 107 | file `.uf2` file into your Pico. You must make sure to build the correct | ||
| 108 | target, or otherwise copy the correct file, because many RP2040 and RP2530 | ||
| 109 | devices exist and Libreboot provides images for **all of them** in the same | ||
| 110 | release tarball. | ||
| 111 | |||
| 112 | **NOTE: Other RP2040/2530 devices will also work. You just have to match | ||
| 113 | the right pins and use the correct firmware file!** | ||
| 114 | |||
| 115 | Logic levels | ||
| 116 | ------------ | ||
| 117 | |||
| 118 | A Pico has proper 3.3V logic levels, unlike a ch341a. Which means it won't | ||
| 119 | destroy your board by sending 5V to it. If you have a 1.8V flash chip, | ||
| 120 | you need to add a logic level converter. **Please ensure that you have matched | ||
| 121 | the voltage of your programmer to the voltage of your chip; both the data lines | ||
| 122 | and power lines to the chip must match.** | ||
| 123 | |||
| 124 | Wiring | ||
| 125 | ------ | ||
| 126 | |||
| 88 | 127 | Disconnect the Pico and proceed to wire it to your | Disconnect the Pico and proceed to wire it to your |
| 89 | 128 | [flash chip](/docs/install/spi.html#identify-which-flash-type-you-have). | [flash chip](/docs/install/spi.html#identify-which-flash-type-you-have). |
| 90 | 129 | ||
| 91 | 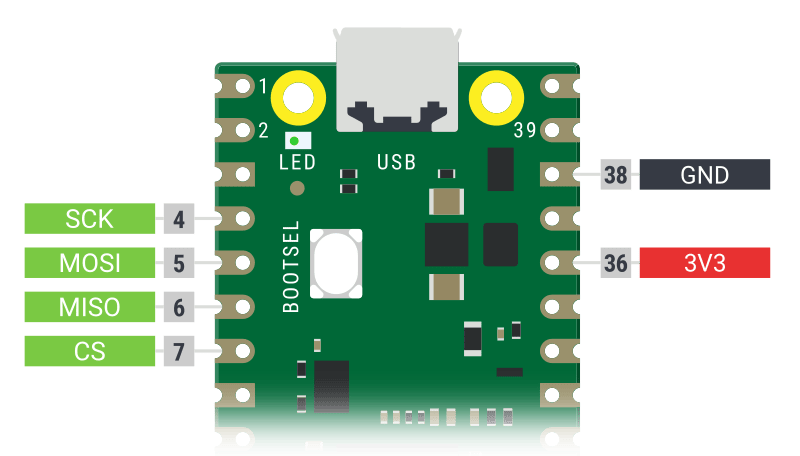 | ||
| 130 | **NOTE: SCK and CLK mean the same thing. The diagram below says SCK, and other | ||
| 131 | parts of this guide say CLK. It's the same thing!** | ||
| 92 | 132 | ||
| 93 |  | ||
| 133 |  | ||
| 135 | |||
| 136 |  | ||
| 138 | |||
| 139 |  | ||
| 94 | 140 | ||
| 95 | 141 | Headers were manually soldered on the top side, and the plastic packaging | Headers were manually soldered on the top side, and the plastic packaging |
| 96 | 142 | was repurposed as an insulating base. These might be nice to have, but by no | was repurposed as an insulating base. These might be nice to have, but by no |
| ... | ... | will appear: | |
| 102 | 148 | ||
| 103 | 149 | [453876.669019] cdc_acm 2-1.2:1.0: ttyACMx: USB ACM device | [453876.669019] cdc_acm 2-1.2:1.0: ttyACMx: USB ACM device |
| 104 | 150 | ||
| 105 | Take note of the ttyACMx. Flashrom is now usable | ||
| 151 | Take note of the ttyACMx. Flashprog is now usable | ||
| 106 | 152 | (substitute ttyACMx with what you observed earlier). | (substitute ttyACMx with what you observed earlier). |
| 107 | 153 | ||
| 108 | 154 | flashprog -p serprog:dev=/dev/ttyACMx,spispeed=16M | flashprog -p serprog:dev=/dev/ttyACMx,spispeed=16M |
| ... | ... | Take note of the ttyACMx. Flashrom is now usable | |
| 110 | 156 | spispeed=32M usually works, but since it's not much faster it's probably | spispeed=32M usually works, but since it's not much faster it's probably |
| 111 | 157 | not worth it. The 12Mbps USB port is limiting the actual speed here. | not worth it. The 12Mbps USB port is limiting the actual speed here. |
| 112 | 158 | ||
| 159 | Higher speeds might work nicely, on Pico 2. | ||
| 160 | |||
| 113 | 161 | 不要使用 CH341A! | 不要使用 CH341A! |
| 114 | 162 | ================== | ================== |
| 115 | 163 | ||
Hints:
Before first commit, do not forget to setup your git environment:
Clone this repository using HTTP(S):
Clone this repository using ssh (do not forget to upload a key first):
Clone this repository using git:
You are allowed to anonymously push to this repository.
This means that your pushed commits will automatically be transformed into a merge request:
Before first commit, do not forget to setup your git environment:
git config --global user.name "your_name_here"
git config --global user.email "your@email_here"
git config --global user.email "your@email_here"
Clone this repository using HTTP(S):
git clone https://rocketgit.com/user/libreboot/lbwww
Clone this repository using ssh (do not forget to upload a key first):
git clone ssh://rocketgit@ssh.rocketgit.com/user/libreboot/lbwww
Clone this repository using git:
git clone git://git.rocketgit.com/user/libreboot/lbwww
You are allowed to anonymously push to this repository.
This means that your pushed commits will automatically be transformed into a merge request:
... clone the repository ...
... make some changes and some commits ...
git push origin main
... make some changes and some commits ...
git push origin main
